The 2024 Customer Service Transformation:
Generative AI's Pivotal Role
The GenAI Revolution in Customer Service

Pros
Enhanced Efficiency: AI-driven tools will significantly speed up response times and improve accuracy in handling customer inquiries.
Personalized Interactions: GenAI can provide tailored responses, creating a more personalized experience for customers.
Cons
Depersonalization Risk: Over-reliance on AI might lead to a lack of personal touch in customer interactions.
Technical Complexity: Implementing and maintaining GenAI solutions requires technical expertise and resources.

Impact: Elevating Customer Experiences
Analogies and Examples:
AI as a Skilled Concierge: Just like a concierge knows guests’ preferences, GenAI can anticipate customer needs and offer personalized assistance.
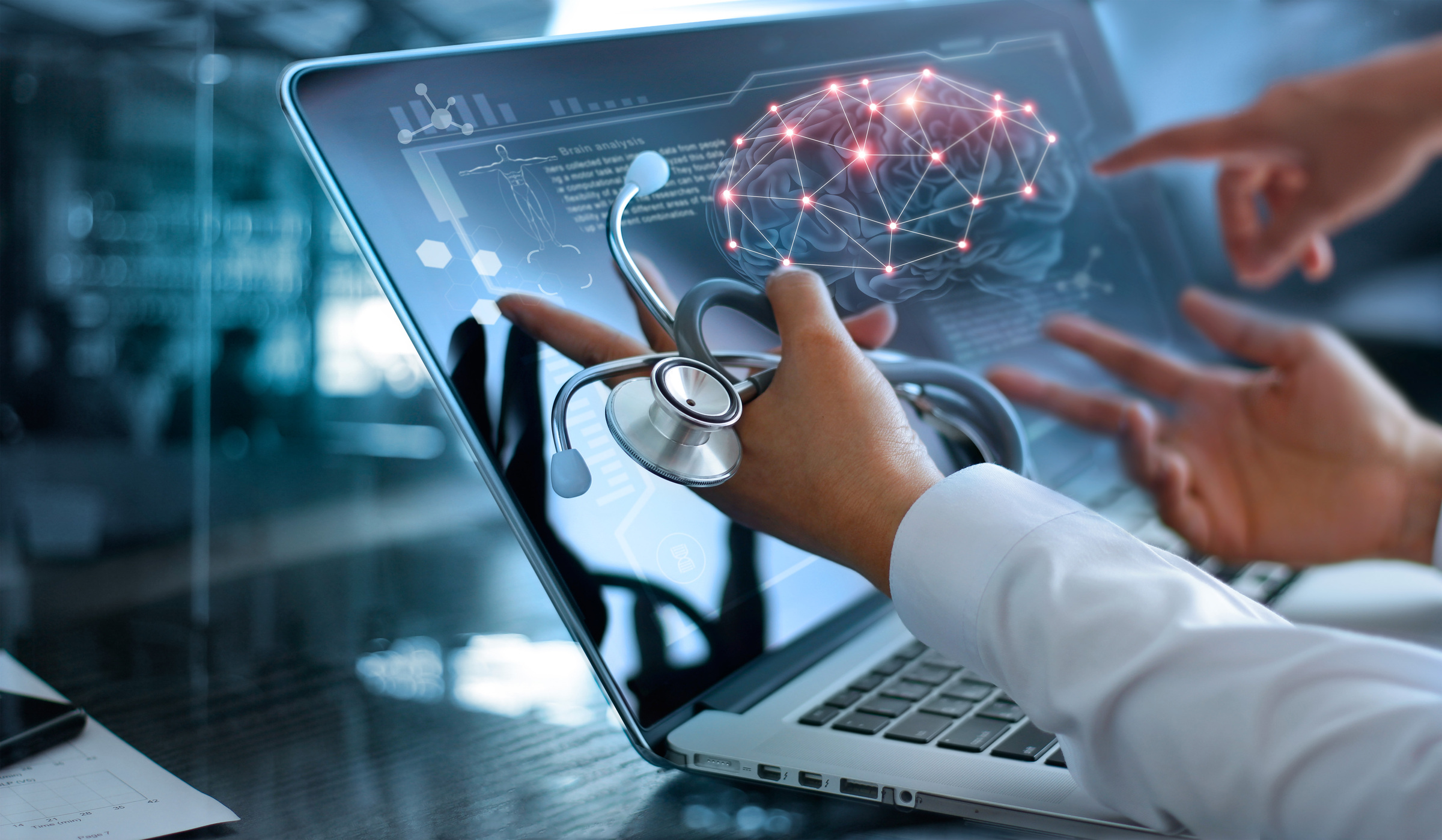
The AI-Assisted Physician: Imagine a doctor (customer service agent) with an AI assistant providing instant information to diagnose and treat patients (solve customer issues) more effectively.

Impact: Elevating Customer Experiences
Analogies and Examples:
AI as a Skilled Concierge: Just like a concierge knows guests’ preferences, GenAI can anticipate customer needs and offer personalized assistance.
The AI-Assisted Physician: Imagine a doctor (customer service agent) with an AI assistant providing instant information to diagnose and treat patients (solve customer issues) more effectively.
Curate's Role: Navigating the GenAI Wave
Curate’s AI Advisory services are crucial in guiding businesses through the adoption and optimization of GenAI in customer service.
- Strategic AI Implementation: We help design strategies that integrate GenAI seamlessly into customer service models.
- Balancing AI and Human Elements: Curate ensures that while AI enhances efficiency, the human element in customer service remains intact.







 Creating an elevated digital experience takes more than one step of automation. Don’t miss our specialized
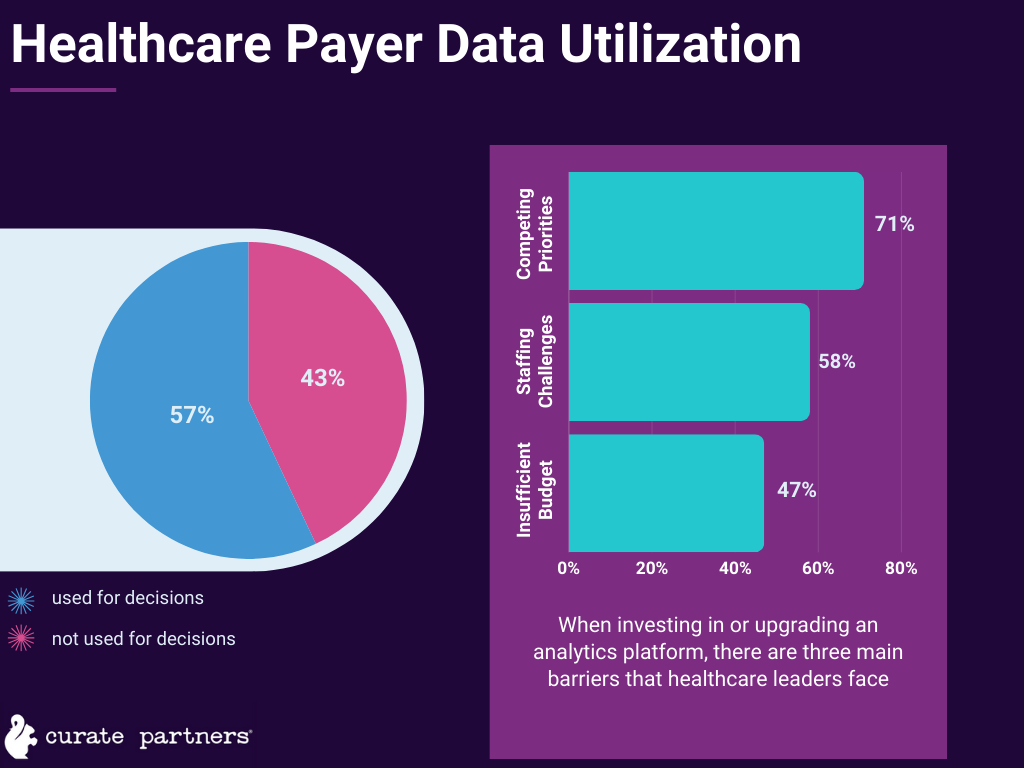
Creating an elevated digital experience takes more than one step of automation. Don’t miss our specialized  From our years of working with payer businesses, we understand that one of the biggest headaches is coordinating and integrating unstructured data.
From our years of working with payer businesses, we understand that one of the biggest headaches is coordinating and integrating unstructured data.
 This is where cognitive agents come in. This automation technology bridges NLP with machine learning, creating virtual entities—agents—that perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence.
This is where cognitive agents come in. This automation technology bridges NLP with machine learning, creating virtual entities—agents—that perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence.


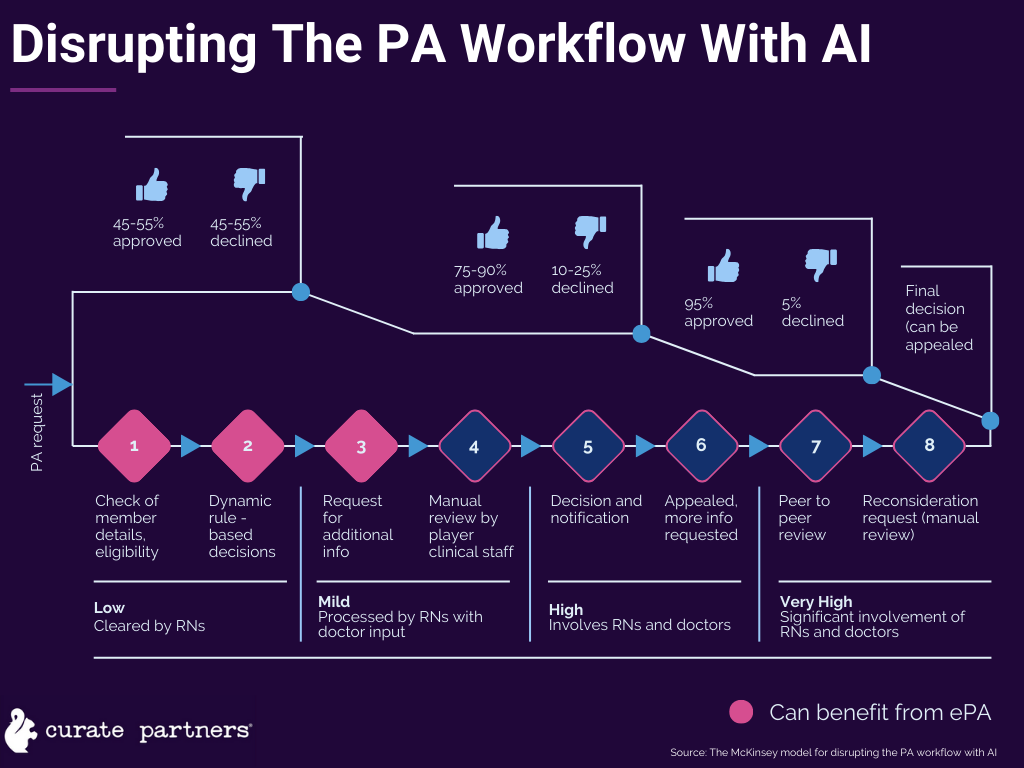
 As intended, electronic PA intends to improve patients’ access to care, keeping the flow of information moving between facilities, payers, and patients.
As intended, electronic PA intends to improve patients’ access to care, keeping the flow of information moving between facilities, payers, and patients.














 Another challenge in maintaining payment integrity is the occurrence of billing errors and inaccurate claims. These errors can arise due to coding mistakes, documentation discrepancies, or misunderstandings of reimbursement guidelines. Inaccurate claims can result in overpayment or underpayment of healthcare providers, leading to financial inaccuracies and disputes.
Another challenge in maintaining payment integrity is the occurrence of billing errors and inaccurate claims. These errors can arise due to coding mistakes, documentation discrepancies, or misunderstandings of reimbursement guidelines. Inaccurate claims can result in overpayment or underpayment of healthcare providers, leading to financial inaccuracies and disputes.